Disruption: 5G
The third part in our disruption series, Senior Analyst Joe Chin discusses the benefits of 5G.
Growth of Wireless
It seems inconceivable today that the world once existed without wireless technology. Such is the impact made on so many industries and in such a short period of time, that it’s easy to take for granted. Wireless technology represents a powerful platform for innovation by liberating disruptive ideas from the shackles of physical infrastructure. It enables unmatched reach, ubiquitous engagement, and unprecedented flexibility. Wireless first revolutionized communications by freeing our voices from cords, greatly expanding our ability to communicate on-demand with the rest of the planet. The mobile phone was invented less than 40 years ago and today over 80% of the world’s population has a wireless connection. Wireless then revolutionized computing by putting a high-performance workstation in everyone’s pocket. Apple gave birth to the modern smartphone less than 15 years ago and we’ve never looked back. Entire industries have risen and fallen in the wake of the smartphone, and one could argue wireless-enabled social media/location-based services are changing the ways humans interact within society today. Going forward, pundits believe wireless will be integral to the “Fourth Industrial Revolution” by tying together new physical, digital, and biological technologies. Future disruption, we believe, will take the form of mobile supercomputing, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and artificial intelligence to name a few. Underlying all of this will be fifth-generation wireless technology (5G), a set of technical ground rules for networks that enable a greater than 10x increase in data rates, low latency and the ability to support hundreds of billions of connected devices.Wireless technology represents a powerful platform for innovation by liberating disruptive ideas from the shackles of physical infrastructure.
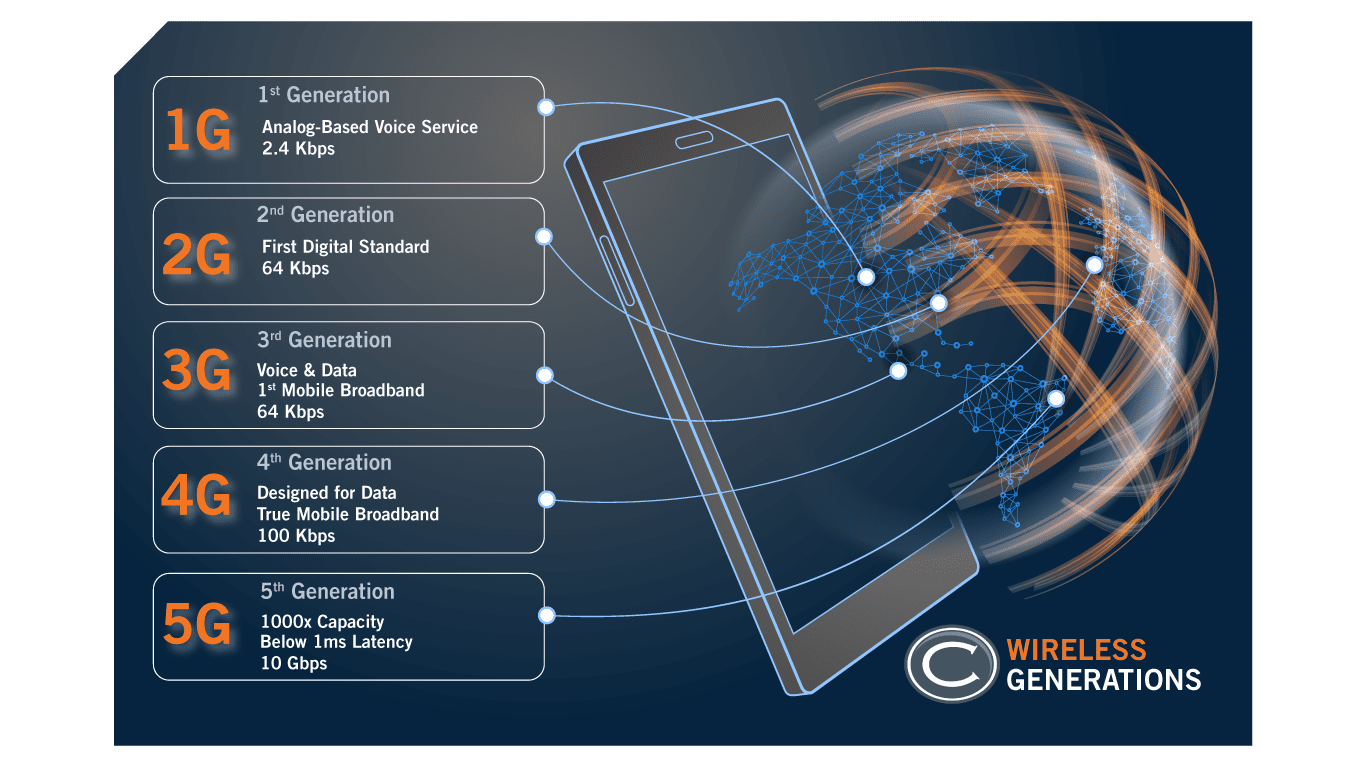
Wireless Generations
5G is the most recent iteration of mobile wireless standards and was created in response to the demand for new broadband services. The primary standards bodies involved in codifying 5G include the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Wireless technology experiences major advancements about once every ten years and a new generation is named during these step functions.
- 1G (~1980) – First generation wireless was an analog standard designed to deliver voice in the 1980s. 1G pioneered wireless telecommunications but had poor voice quality, limited battery life, and large form factors.
- 2G (~1990) – Second generation wireless was digital standard, circuit-switched technology introduced in the 1990s. 2G greatly increased the quality and capacity of voice traffic but had limited data capability.
- 3G ( ~2000) – Third generation wireless introduced high-speed wireless data in the 2000s. 3G networks enabled true internet access on mobile devices for the first time with data rates up to 2Mbps.
- 4G (~2010) – Fourth generation (4G) wireless services is what we currently enjoy, with true mobile broadband speeds that can compete with fixed-line. 4G delivers data up to 100 Mbps but suffers from spectral inefficiency and high-power consumption.
Looking ahead, 5G standards are in place now and commercial services are launching around the world. Asian network operators in Korea, Japan, and China are the early adopters. We expect U.S. carriers to be close behind with 5G service starting sometime in 2020. Europe and the rest of the world will then follow suit.
5G will elevate the mobile network, even more, to interconnect people as well as machines, objects, and devices. It will deliver unprecedented levels of performance to empower new user experiences and connect new industries. This generation will embody advanced features such as multi-Gbps peak data rates, ultra-low latency under one millisecond, improved power efficiency, massive capacity, and more uniform user experiences. 5G builds on previous generations of wireless with several new advances. Network densification will be required with the significant addition of small cells and a provision for machine to machine (M2M) communications. Radio access technology will integrate massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antennas and millimeter-wave frequency bands (20-50 GHz) to support high data rates. Progress on hardware will be complemented by developments in system architecture to build distributed and flexible networks. Cloud-based radio access networks, software-defined networking, and network function virtualization will all play a role. 5G is not a single technology, rather it requires the interweaving of simultaneous advancements across several disciplines to form the fabric of this disruptive change. It’s a disruption that comes with great complexity but opportunity as well.5G is not a single technology, rather it requires the interweaving of simultaneous advancements across several disciplines to form the fabric of this disruptive change.
What 5G means for the masses
As we look forward, it’s difficult to predict exactly how 5G will impact business and society. Ten years ago, with the dawn of 4G, how many of us foresaw the rise of ride-hailing services that would roil transportation markets around the world? Who could have imagined that we would be streaming high definition video while riding down the highway? Who knew human communication and social affirmation would be defined through “tweets”, “snaps”, “check-ins” and “likes”? Who could’ve imagined something called “Fortnite” would become a member of the family? The only thing we can say for certain is that 5G is a disruptive force that will make all the other “next big things” in technology possible.
With that said, three areas that could blossom in a 5G world are Autonomous Vehicles, Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) and eHealth. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines self-driving automation from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full). Today’s state of the art systems are Level 2, or partial automation, requiring the driver to remain engaged at all times. We believe true Level 5 automation is in the distant future and will require the ultra-low latency and M2M communication of 5G networks to interpret and react in real world driving conditions. In manufacturing, competitiveness means everything and wireless connectivity enables increased efficiency. Firms are betting on 5G to deliver smart factories characterized by real-time telemetry generated by sensors on the floor, robotic automation, and AR/VR wearables. In health, the possibilities are endless. Wearable monitoring devices, mobile telemedicine, and remote robotic procedures can improve healthcare resource efficiency and outcomes. Healthcare spending represents 18% of GDP and cost inflation curves are ripe for disruption.
Certain information contained in this communication constitutes “forward-looking statements”, which are based on Cambiar’s beliefs, as well as certain assumptions concerning future events, using information currently available to Cambiar. Due to market risk and uncertainties, actual events, results or performance may differ materially from that reflected or contemplated in such forward-looking statements. The information provided is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, investment, legal or tax advice. Nothing contained herein should be construed as a recommendation or endorsement to buy or sell any security, investment or portfolio allocation.
Any characteristics included are for illustrative purposes and accordingly, no assumptions or comparisons should be made based upon these ratios. Statistics/charts may be based upon third-party sources that are deemed reliable; however, Cambiar does not guarantee its accuracy or completeness. As with any investments, there are risks to be considered. Past performance is no indication of future results. All material is provided for informational purposes only and there is no guarantee that any opinions expressed herein will be valid beyond the date of this communication.